Discover the world of 3D animation—how it works, where it's used, and why it's transforming everything from film and gaming to education and marketing. This in-depth guide explains the full animation process, compares 2D vs 3D, and explores the future of real-time animation. Ideal whether you're new to 3D animation or a seasoned professional.
What is 3D Animation?
3D animation is the craft of creating digitally generated motion in a three-dimensional environment. It’s where imagination meets technology—bringing characters, environments, and objects to life in a virtual space. Unlike traditional 2D animation that moves within a flat plane, 3D animation offers depth and dimension, creating visuals that are often indistinguishable from real life.
This article explores everything from the basics to advanced techniques, applications, and the evolving landscape of 3D animation.

Hippobag – raw shot

Hippobag – final shot
How Does 3D Animation Work?
At its core, 3D animation involves building virtual objects, called models, defining how they move through rigging and animation, and producing sequences of frames – a process called rendering – that result in lifelike motion.
The 3D Animation Pipeline
- Modelling: Artists start by designing 3D models. These can be characters, vehicles, landscapes, or any other asset. This process involves shaping geometry in a 3D space using software like Blender, Maya, or 3DS Max.
- Texturing: Textures and materials are applied to these models to define surface qualities—metallic, glossy, rough, soft, etc. This makes a model look more realistic or stylised, depending on the artistic vision.
- Rigging: Think of this step as building a skeleton for the model. It allows characters or objects to move naturally by assigning bones and joints to the model’s structure.
- Animation: Animators bring the rigged models to life by defining their motion using keyframes or motion capture data. Whether it’s a person running or a bird flying, every movement is created meticulously to feel smooth and believable.
- Lighting: Just like in cinematography, lighting plays a crucial role. It affects the mood, depth, and realism of the scene.
- Rendering: This step transforms all the scene data into individual frames or videos. It’s computationally intense and can take hours or even days for high-end productions.
- Compositing: Finally, all rendered elements are layered, effects are added, colours are corrected, and the animation is polished for the final output.
CGI Product Breakdown Animation
3D Animation vs. 2D Animation
| Aspect | 2D Animation | 3D Animation |
| Visual Depth: | Flat – height and width | Full depth – height, width, and depth |
| Style: | Typically stylised and hand-drawn | Can range from cartoon-like to hyper-realistic |
| Movement: | Often exaggerated and frame-by-frame | Fluid, with natural transitions |
| Production Tools: | Photoshop, After Effects, Toon Boom | Blender, Maya, Cinema 4D, Unreal Engine |
| Time & Cost: | Usually quicker and less expensive | More resource-intensive and complex |
While 2D remains ideal for stylistic content, 3D animation offers realism and immersion—especially suited for today’s high-expectation audiences.
For more information, read how to make 2D Animation and how to make a 3D (CGI) Animation
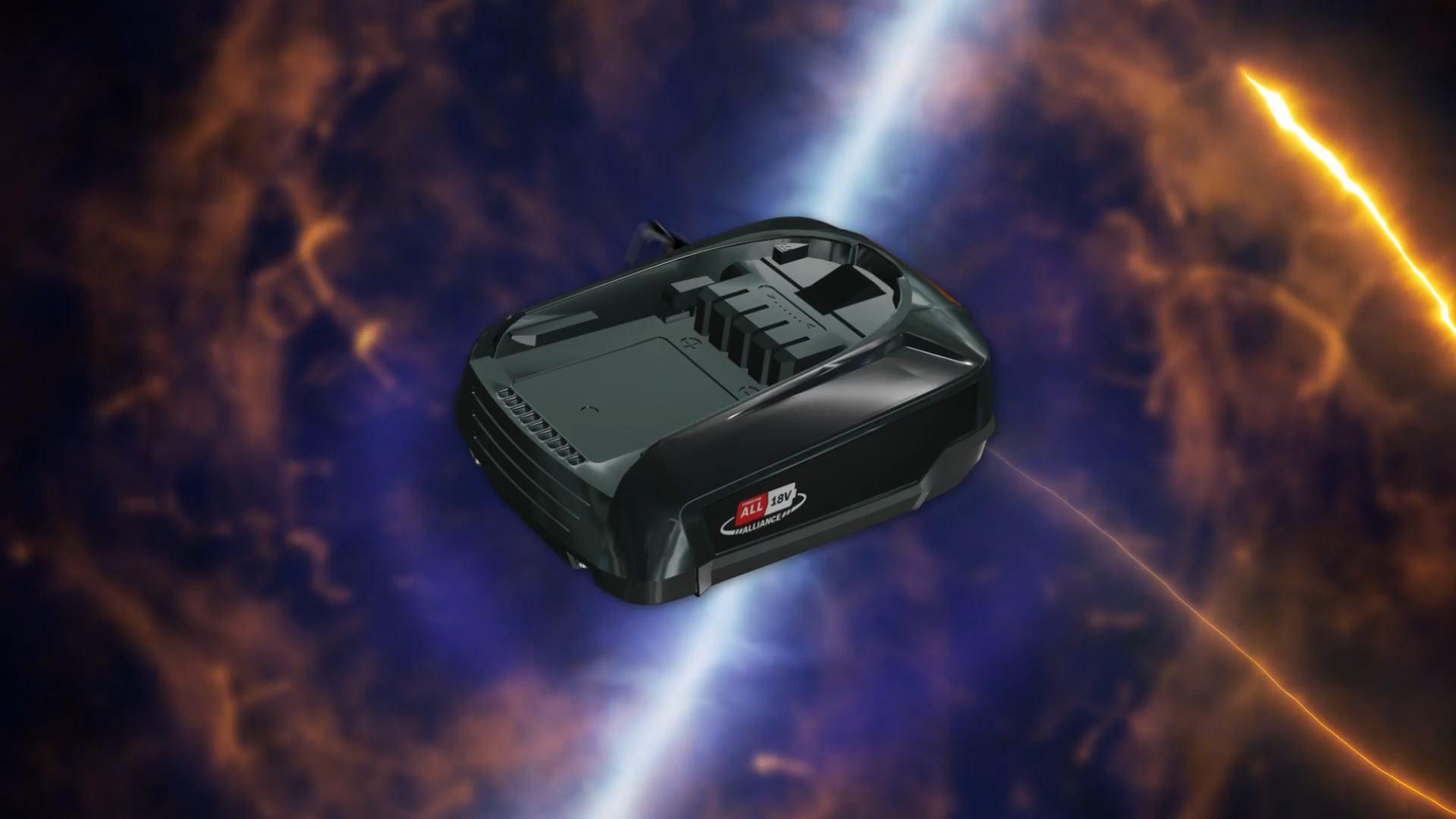

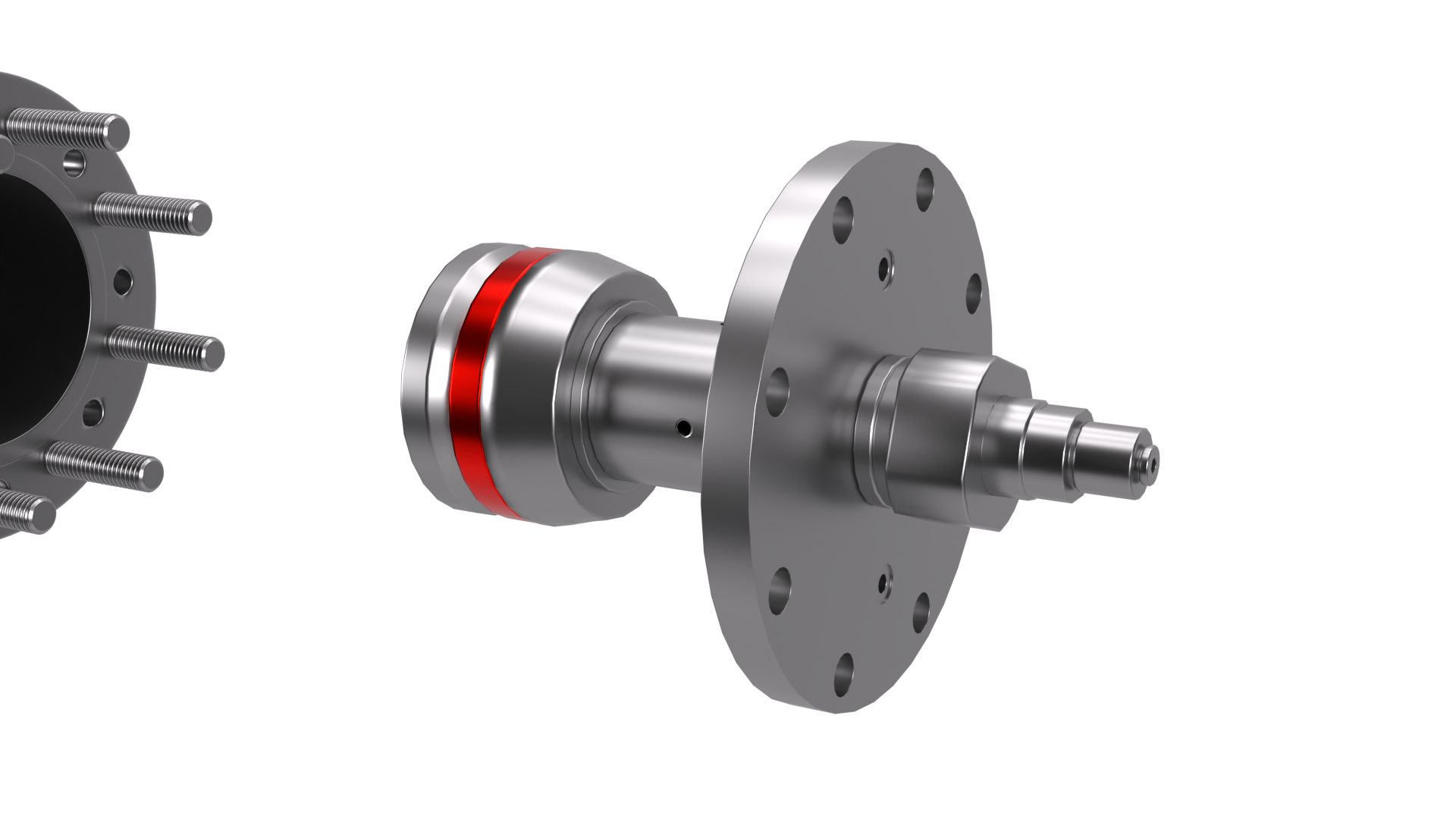
CGI Render of a Garden Tool Battery
Where is 3D Animation Used?
3D animation is deeply embedded across multiple industries:
Entertainment
Used extensively in films, TV series, and especially in video games, 3D animation delivers blockbuster visuals and deeply immersive experiences.
Advertising & Marketing
Brands use animated product demos, explainer videos, and CGI-enhanced commercials to capture attention and drive engagement.
Architecture & Engineering
Architects use 3D animation for walkthroughs, simulations, and visualising buildings before they’re constructed.
Science & Medicine
From cellular-level visualisations to surgical simulations, 3D animation brings complex data to life.
Education
In e-learning and educational content, 3D animation helps explain difficult topics, especially in STEM subjects.
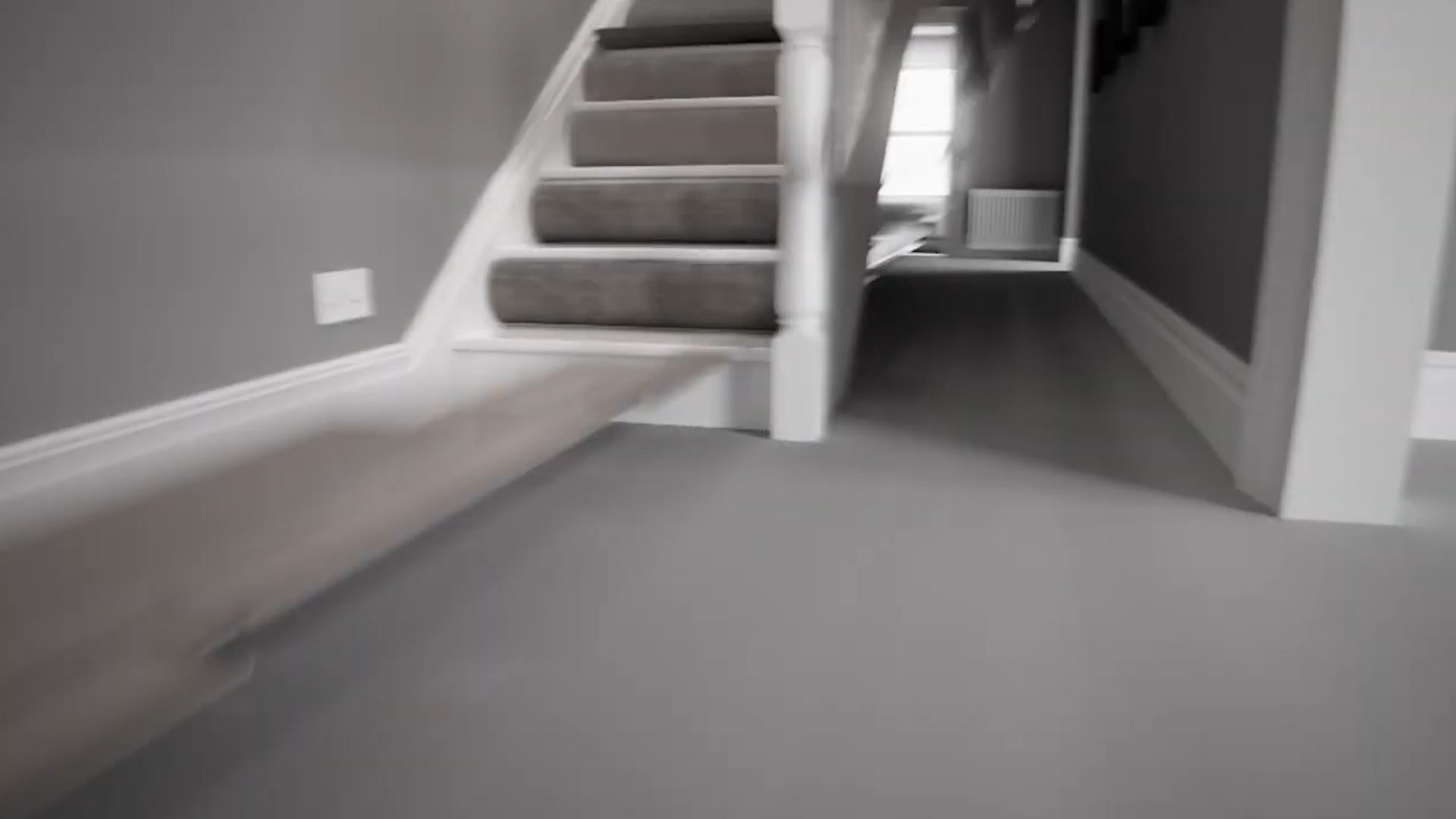

CGI Render of a Home Interior (with Video Screenshot Motion Blur)

CGI Render of a Home Interior with Hardwood Floors
Real-Time 3D Animation
A major evolution in this field is real-time animation, where scenes are rendered instantly using game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine.
Unlike traditional methods that require lengthy rendering, real-time 3D animation allows creators to preview and adjust animation live—making it essential in video games, virtual reality, virtual production for film, and live broadcasts.
Benefits include:
- Faster iteration cycles
- Interactive storytelling
- Multi-platform output (VR, AR, mobile, web)
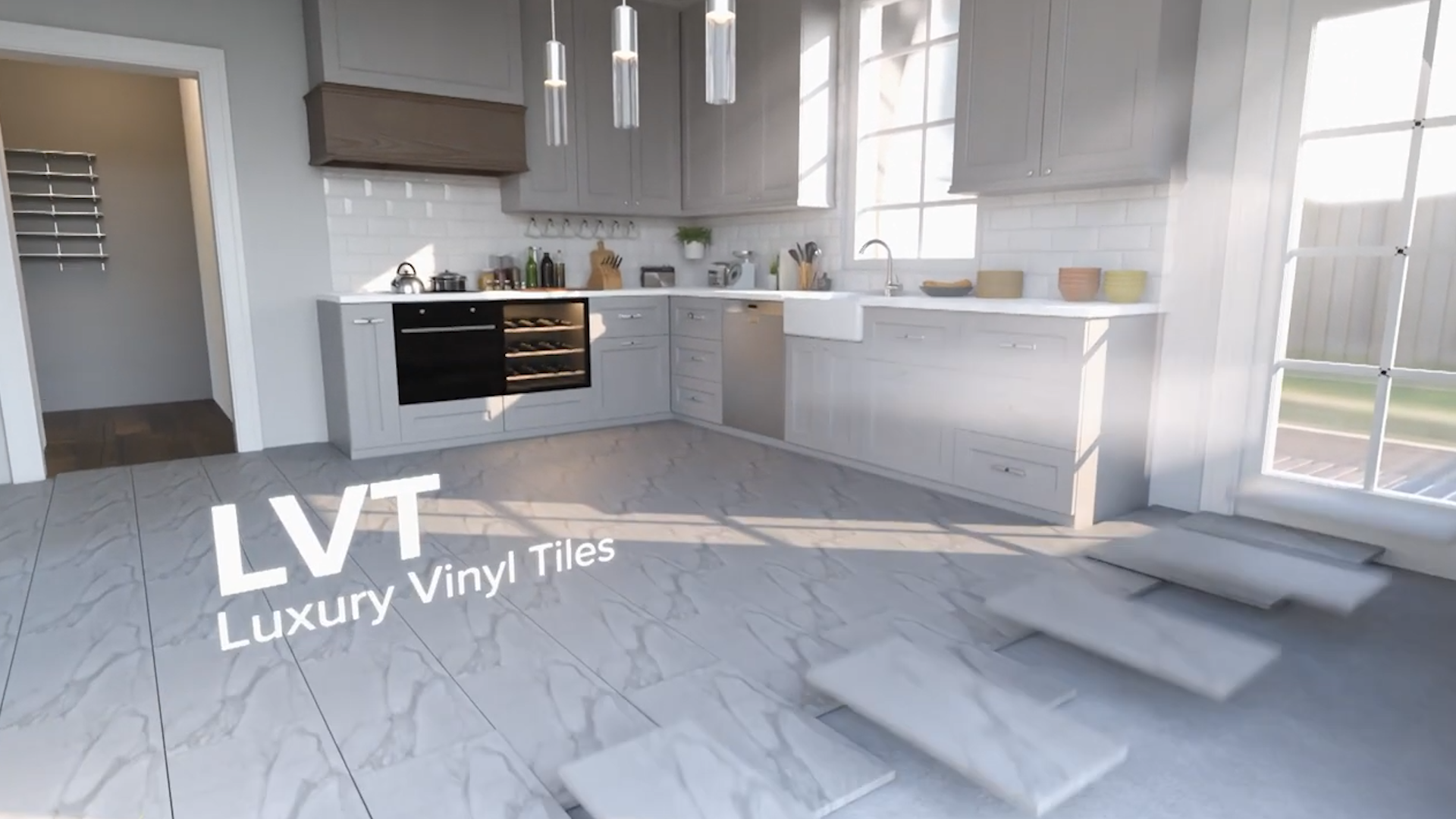

CGI Render of a Home Interior with Luxury Vinyl Tiles
Why 3D Animation Matters
3D animation has transformed visual storytelling. Its ability to create stunning, lifelike scenes that wouldn’t be possible through live action or 2D makes it invaluable.
Advantages include:
- Immersive and engaging experiences
- High visual fidelity
- Scalability across industries
- Strong emotional impact
In marketing, it can drastically improve viewer retention. In education, it boosts understanding. In entertainment, it shapes some of the most memorable cinematic moments in recent memory.
CGI Render of an InPipe Product
Tools for Creating 3D Animation
- Blender – Open-source and full-featured; ideal for indie creators
- Autodesk Maya – Industry leader in film and AAA games
- Cinema 4D – Easy to learn, great for motion graphics
- Houdini – Advanced VFX and procedural generation
- Unity & Unreal Engine – Real-time animation and game development
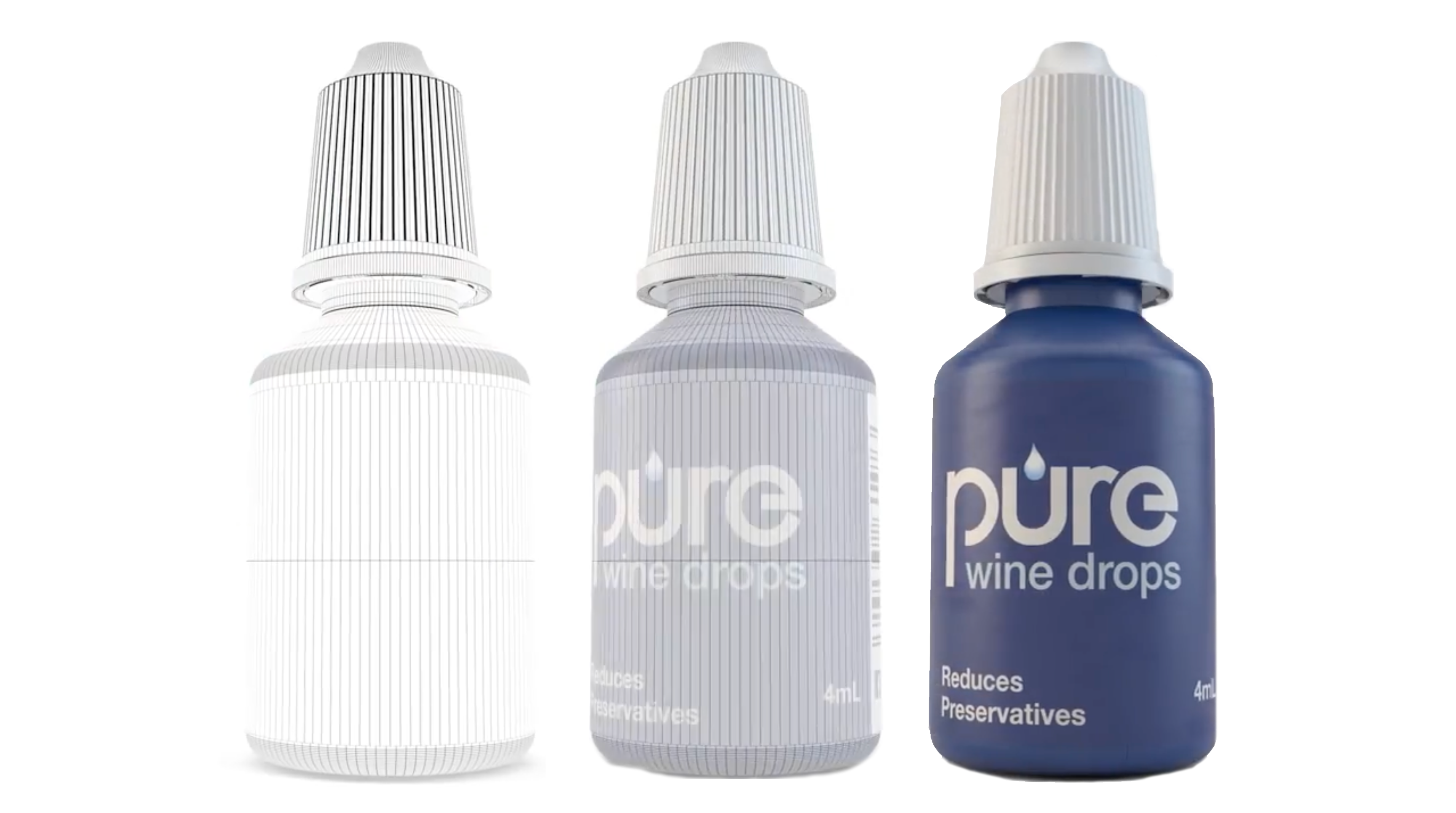

3D Model of Pure Wine Drops Bottle: The Transition From CAD to Near Photorealistic Design
Future of 3D Animation
The future is increasingly interactive, real-time, and intelligent. With AI, machine learning, and virtual production tools becoming more accessible, expect 3D animation to expand into:
- Virtual influencers and avatars
- AI-assisted animation workflows
- Real-time filmmaking and virtual sets
- Holographic and spatial media
3D animation will continue to shape how we communicate, entertain, and imagine.
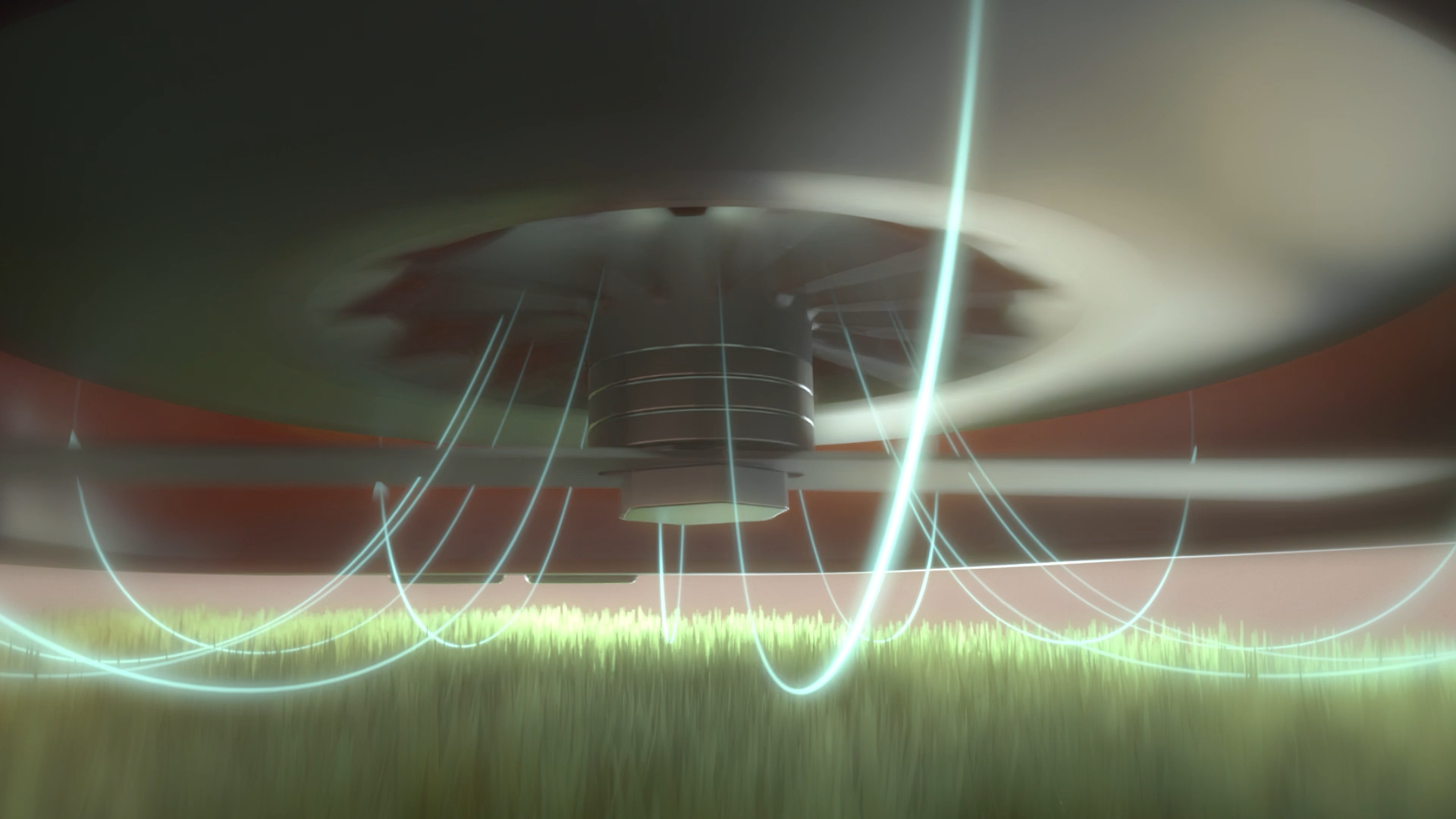

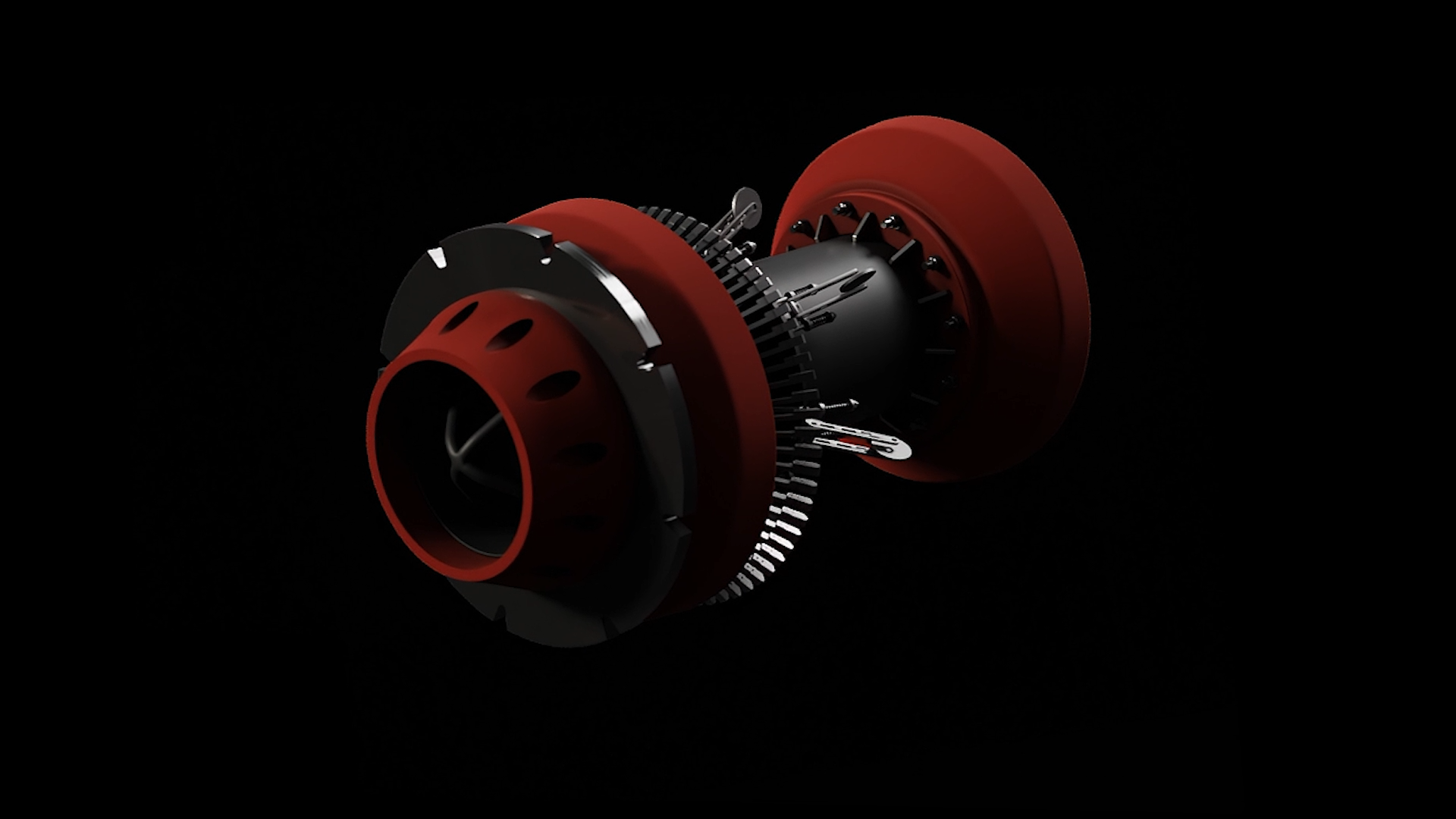
CGI Animation Representing Flymo Suction
Conclusion
3D animation is more than a visual technique—it’s a transformative storytelling tool that blends creativity with technology. Whether you’re a filmmaker, marketer, educator or designer, understanding the foundations of 3D animation unlocks new ways to inform, captivate, and inspire.
If you wish to know more about how 3D animation can enhance your business, please get in touch to speak with our experts.
